Substituted vinyl piperazine-piperidine urea derivatives as anticancer agents
EP21201359.3
The invention is comprised in the field of medicinal chemistry, and it is related to substituted vinyl piperazine-piperidine urea compounds which are well effective as antitumoral agents. In particular, they are suitable in methods of treatment of glioblastoma (GB), multiple myeloma (MM) or pancreatic cancer (PC).
Background
Glioblastoma (GB), multiple myeloma (MM) and pancreatic cancer (PC) continue to represent an unmet medical need; no effective drugs are available yet, and the current therapies are associated to relevant side effects and limited overall efficacy. Our invention is aimed at filling this important therapeutic gap. The present invention discloses novel small molecules with drug-like properties that demonstrated greater efficacy in vitro than the current gold-standard of therapy in patient-derived tumor cell lines. The compounds have been identified so far at the “hit-to-lead” stage.
The main target indication of the patented compounds is the treatment of PC, which is one of the most lethal tumors still missing any improvement in the prognosis over the past 20 years. Its complex etiology, difficulty in early diagnosis, limited treatment options, and expected increasing incidence make the need for new, effective therapies particularly pressing. Additionally, the patented compounds showed activity against two other particularly aggressive tumors, namely GB and MM. GB is another important unmet medical need, and represents the second target indication of our invention, as it is the most common and most aggressive type of primary brain cancer, with no effective treatment yet. Lastly, MM is the third most common form of blood cancer, often characterized by relapses and resistance to therapy. Therefore, the patented compounds are active against particularly aggressive tumors.
Our Technology
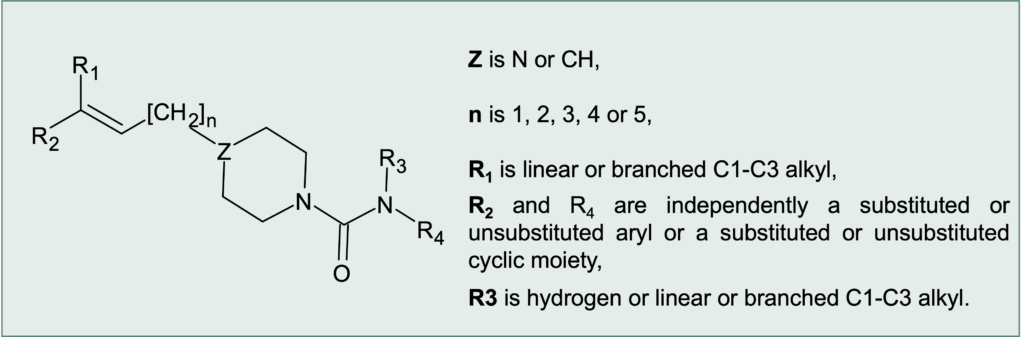
The disclosed small molecules, and therefore their development is easier than biotechnological drugs. An eco-sustainable, versatile and efficient synthetic route has been developed to limit the production of waste and optimize the use of reagents and energy, with particular attention to the atom economy and the E factor of the process.
Cytotoxic activity evidenced that some compounds are comparable to gemcitabine and 5-fluorouracil against PC and 70-folds more active in vitro than the gold standard temozolomide on GB.
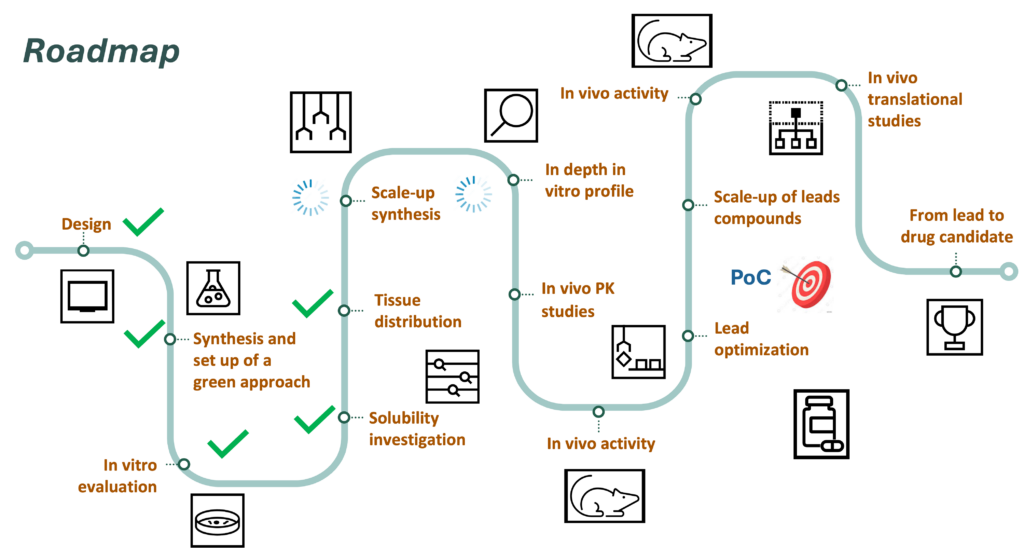
Future perspectives